Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (11): 1653-1658.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.11.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Autologous bone marrow aspirate concentrate repairs peri-implant bone defect
Yang Ying1, Zhong Wei-jian2, Liu Guo3, Ma Guo-wu2
- 1Department of Oral Implantology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, Zhejiang Province, China; 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Stomatology College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116085, Liaoning Province, China; 3Department of Conservative & Endodontic Dentistry, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Revised:2014-01-11Online:2014-03-12Published:2014-03-12 -
Contact:Ma Guo-wu, M.D., Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Stomatology College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116085, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Yang Ying, Master, Physician, Department of Oral Implantology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, Zhejiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Ying, Zhong Wei-jian, Liu Guo, Ma Guo-wu. Autologous bone marrow aspirate concentrate repairs peri-implant bone defect[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(11): 1653-1658.
share this article
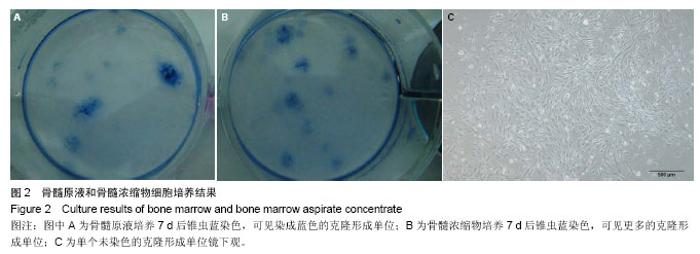
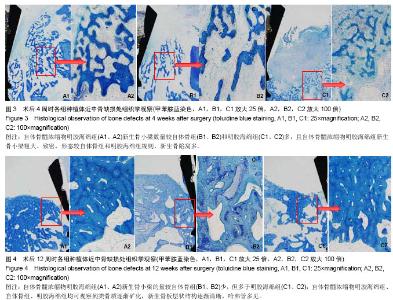
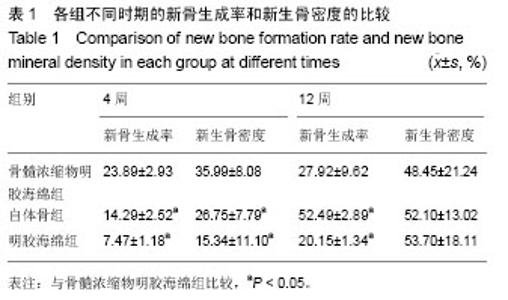
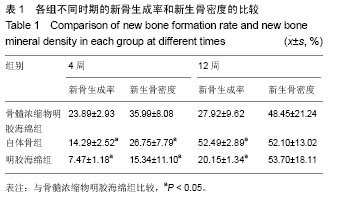
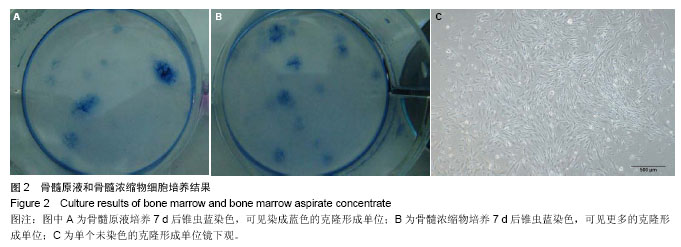
2.1 大体观察 实验动物无死亡,术后3 d实验犬饮食及生活习性恢复正常,伤口无感染症状,无排斥反应。48颗种植体均无感染,创口愈合良好,种植体周围牙龈无充血肿胀、破溃及流脓等炎症反应。去除软组织后,种植体生长良好,金属杆敲击种植体时声音清脆,未见松动现象。 2.2 细胞学检测结果 骨髓浓缩物组白细胞的浓度为骨髓原液组白细胞浓度的(2.78±0.22)倍(n=12)。骨髓原液组白细胞浓度平均值为(41.50±10.92)×109 L-1,骨髓浓缩物组白细胞浓度平均值为(114.41±27.61)×109 L-1。 将相同体积的骨髓原液和骨髓浓缩物稀释20倍后培养7 d时均能观察到克隆形成单位,但骨髓浓缩物组可观察到更多的克隆形成单位(图2)。7 d时骨髓浓缩物组含有20-40个细胞的克隆形成单位约为2.7/cm2,而骨髓原液组含有20-40个细胞的克隆形成单位约为2.6/cm2。11 d时骨髓浓缩物组含有20-40个细胞的克隆形成单位约为2.4/cm2,含有超过40个细胞的克隆形成单位约为3.8/cm2,而骨髓原液组含有20-40个细胞的克隆形成单位约为1.4/cm2,含有超过40个细胞的克隆形成单位约为2.0/cm2。 2.3 组织学观察结果 4周时,骨髓浓缩物明胶海绵组的新骨生成率和新生骨密度均高于自体骨组和明胶海绵组(图3),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。12周时骨髓浓缩物 明胶海绵组新骨生成率低于自体骨组,但高于明胶海绵组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),骨髓浓缩物明胶海绵组与自体骨组、明胶海绵组的新生骨密度相差不大(图4),差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,表1)。"
| [1] Buser D, Dula K, Hess D,et al. Localized ridge augmentation with autografts and barrier membranes.Periodontol 2000. 1999; 19:151-163.[2] Laurie SW, Kaban LB, Mulliken JB,et al.Donor-site morbidity after harvesting rib and iliac bone.Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984; 73(6):933-938.[3] Younger EM, Chapman MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites.J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3(3):192-195.[4] Arrington ED, Smith WJ, Chambers HG,et al.Complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (329):300-309.[5] Finkemeier CG. Bone-grafting and bone-graft substitutes.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(3):454-464.[6] Colnot C, Romero DM, Huang S, et al. Mechanisms of action of demineralized bone matrix in the repair of cortical bone defects.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(435):69-78.[7] Buck BE, Malinin TI, Brown MD. Bone transplantation and human immunodeficiency virus. An estimate of risk of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(240):129-136.[8] Buck BE, Resnick L, Shah SM,et al. Human immunodeficiency virus cultured from bone. Implications for transplantation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(251):249-253. [9] Hernigou P, Poignard A, Beaujean F,et al. Percutaneous autologous bone-marrow grafting for nonunions. Influence of the number and concentration of progenitor cells.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7):1430-1437.[10] Quarto R, Mastrogiacomo M, Cancedda R,et al. Repair of large bone defects with the use of autologous bone marrow stromal cells.N Engl J Med. 2001;344(5):385-386.[11] Schimming R, Schmelzeisen R.Tissue-engineered bone for maxillary sinus augmentation.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 62(6):724-729.[12] Marcacci M, Kon E, Moukhachev V, et al. Stem cells associated with macroporous bioceramics for long bone repair: 6- to 7-year outcome of a pilot clinical study. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(5):947-955.[13] Hibi H, Yamada Y, Ueda M, et al. Alveolar cleft osteoplasty using tissue-engineered osteogenic material.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;35(6):551-555. [14] Lee J, Sung HM, Jang JD, et al. Successful reconstruction of 15-cm segmental defects by bone marrow stem cells and resected autogenous bone graft in central hemangioma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68(1):188-194. [15] Connolly JF, Guse R, Tiedeman J,et al. Autologous marrow injection as a substitute for operative grafting of tibial nonunions.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(266):259-270. [16] Hernigou P, Poignard A, Beaujean F,et al. Percutaneous autologous bone-marrow grafting for nonunions. Influence of the number and concentration of progenitor cells.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7):1430-1437.[17] Fortier LA, Barker JU, Strauss EJ,et al.The role of growth factors in cartilage repair.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(10):2706-2715.[18] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[19] Chang F, Ishii T, Yanai T,et al.Repair of large full-thickness articular cartilage defects by transplantation of autologous uncultured bone-marrow-derived mononuclear cells.J Orthop Res. 2008;26(1):18-26. [20] Tateishi-Yuyama E, Matsubara H, Murohara T,et al.Therapeutic angiogenesis for patients with limb ischaemia by autologous transplantation of bone-marrow cells: a pilot study and a randomised controlled trial.Lancet. 2002;360 (9331):427-435. [21] Rafii S, Lyden D.Therapeutic stem and progenitor cell transplantation for organ vascularization and regeneration. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):702-712. [22] Higashi Y, Kimura M, Hara K,et al.Autologous bone-marrow mononuclear cell implantation improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with limb ischemia.Circulation. 2004;109(10):1215-1218. [23] Umemura T, Nishioka K, Igarashi A,et al.Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell implantation induces angiogenesis and bone regeneration in a patient with compartment syndrome.Circ J. 2006;70(10): 1362-1364. [24] Reyes M, Lund T, Lenvik T,et al.Purification and ex vivo expansion of postnatal human marrow mesodermal progenitor cells.Blood. 2001 ;98(9):2615-2625. [25] Yasuhara S, Yasunaga Y, Hisatome T,et al. Efficacy of bone marrow mononuclear cells to promote bone regeneration compared with isolated CD34+ cells from the same volume of aspirate.Artif Organs. 2010;34(7):594-599. [26] Muschler GF, Boehm C, Easley K. Aspiration to obtain osteoblast progenitor cells from human bone marrow: the influence of aspiration volume.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79(11):1699-1709. [27] Soltan M, Smiler DG, Gailani F. A new "platinum" standard for bone grafting: autogenous stem cells.Implant Dent. 2005; 14(4): 322-325.[28] Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T,et al.Concentration of bone marrow total nucleated cells by a point-of-care device provides a high yield and preserves their functional activity. Cell Transplant. 2008;16(10):1059-1069.[29] Thoesen MS, Berg-Foels WS, Stokol T,et al.Use of a centrifugation-based, point-of-care device for production of canine autologous bone marrow and platelet concentrates. Am J Vet Res. 2006;67(10):1655-1661.[30] 尹世昌,焦振华,王功国,等. 浓缩自体骨髓移植配合中药治疗骨不连临床研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(6):23-25.[31] Jäger M, Herten M, Fochtmann U,et al.Bridging the gap: bone marrow aspiration concentrate reduces autologous bone grafting in osseous defects.J Orthop Res.2011;29(2):173-180. [32] Jäger M, Jelinek EM, Wess KM,et al. Bone marrow concentrate: a novel strategy for bone defect treatment.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009;4(1):34-43.[33] 张远成,刘国辉,茹长英,等.自体浓缩骨髓干细胞复合人工骨植入治疗骨不连[J].中国医药,2010,5(2):158-159.[34] Murawski CD,Duke GL,Deyer TW,et al. Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) as a Biological Adjunct to the Surgical Treatment of Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus.Techniques Foot & Ankle Surg. 2011;10(1):18-27.[35] Adams SB, Lewis JS Jr, Gupta AK,et al. Cannulated screw delivery of bone marrow aspirate concentrate to a stress fracture nonunion: technique tip.Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34(5): 740-744. [36] Smyth NA, Murawski CD, Haleem AM,et al. Establishing proof of concept: Platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow aspirate concentrate may improve cartilage repair following surgical treatment for osteochondral lesions of the talus.World J Orthop. 2012;3(7):101-108.[37] Murawski CD, Kennedy JG. Percutaneous internal fixation of proximal fifth metatarsal jones fractures (Zones II and III) with Charlotte Carolina screw and bone marrow aspirate concentrate: an outcome study in athletes.Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(6):1295-1301.[38] Campbell KJ, Boykin RE, Wijdicks CA,et al. Treatment of a hip capsular injury in a professional soccer player with platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow aspirate concentrate therapy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(7): 1684-1688. [39] Kretlow JD, Spicer PP, Jansen JA, et al. Uncultured marrow mononuclear cells delivered within fibrin glue hydrogels to porous scaffolds enhance bone regeneration within critical-sized rat cranial defects.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010; 16(12):3555-3568.[40] Rickert D, Sauerbier S, Nagursky H,et al. Maxillary sinus floor elevation with bovine bone mineral combined with either autogenous bone or autogenous stem cells: a prospective randomized clinical trial.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22(3): 251-258.[41] Sauerbier S, Rickert D, Gutwald R,et al. Bone marrow concentrate and bovine bone mineral for sinus floor augmentation: a controlled, randomized, single-blinded clinical and histological trial--per-protocol analysis.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(17-18):2187-2197. |
| [1] | Fang Huai-xi, Zhang Ming, Yue Guo-ping . Dexamethasone-soaked gelatin sponges prevent epidural adhesion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1165-1169. |
| [2] | Fang Ming, Wang Zhi-ying, Yu Jin, Li Min, Jin Ding. Osteoprotegerin expression in the peri-implant sulcus fluid after mechanical stimulations at different angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1255-1260. |
| [3] | Lin Yang-dong, Wu Ye-ke. Factors affecting the stability of mini-implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1295-1300. |
| [4] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Zhang Ya-xiao, Wang Ren-feng, Zhang Bing, Liu Jia-bao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation suppresses emphysema-induced inflammation and apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 906-911. |
| [5] | Qu Xin, Wang Xin-chao, Han Lu, Zhang Hai-chao. Different sources of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of liver fibrosis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 926-931. |
| [6] | Zhang Ping-ping, Xiang Chuan. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis: its possibility and future [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 968-973. |
| [7] | Zhang Qiong, Xu Shuo-gui . Biodynamic properties of vascular anastomosis using a new-type degradable anastomosis clip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8487-8490. |
| [8] | Wang Fang-hui, Zhang Shan-shan, Shu Jing-yuan, Gao Yan, Sun Xiao-kun, Wang Qing-shan. Effects of surface modification of titanium implants on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8491-8497. |
| [9] | Yan Zhi-dong, Yan Jia, Zhuansun Yong-xun, Chen Rui, Zhang Wei, Feng Su-ling, Li Jian-guo . Small interfering RNA inhibits the expression of surface antigens CD80/CD86 from mature dendritic cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 754-760. |
| [10] | Cheng Si-yuan, Wen Hai-lin, Si Jing-qiu, Liang Rui, Nie Jing, Wang Hang, Long Jie, Tang Wei, Wei Yong-tao, Tian Wei-dong. Biomechanical evaluation and optimal design of two parameters of dental implant with arbitrarily adjusted angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5473-5479. |
| [11] | Yin Gang, Chen Hui-hao, Guo Xing-feng, Wei Chang-zheng, Hou Chun-lin. Hemostasis and in vivo degradation of thermosensitive chitosan hemostatic film [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5461-5465. |
| [12] | Du Jun-sheng, Wang Guang-yong, Zhong Bing. Gelatin sponge impregnated with hemocoagulase reduces postoperative blood loss of patients with lumbar fractures undergoing posterior spinal decompression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5530-5534. |
| [13] | Li A-li. Absorbable ligating clip in laparoscopic hysterectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5561-5565. |
| [14] | Liu Bin, Li Gang, Xu Bo, Liu Guo-yan. Glucocorticoids-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: adipogenic differentiation and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(29): 4730-4735. |
| [15] | Li Jia-feng, Cui Qun, Sun Xiu-ying, Xu Lei, Sun Jin-hu, Han Jian-guo. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polycaprolactone electrospinning scaffolds repair bone defects around the immediate implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2557-2562. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||